vSAN architecture includes critical services and mechanisms and it’s good to know and understand the key components that operates in the background. vSAN versions have changed over the years and there are newer and newer features but the architecture and core components are the same.
So what happens at the lower level when we create vmdk.
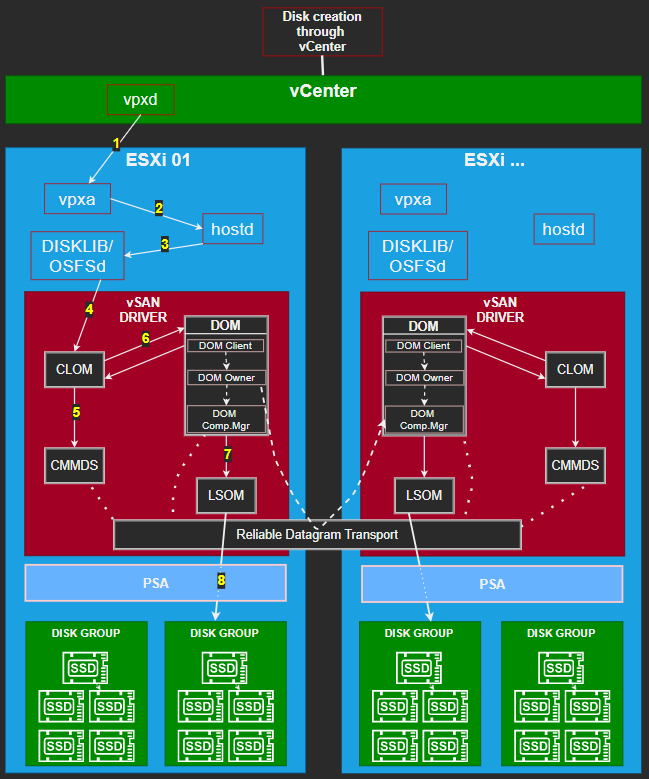
1. vCenter (vpxd) translates tasks to action vpxa agent (on the hosts)
2. vpxa communicates with the ESXi host agent (hostd) translating task to action internally.
QUICK REMINDER: vpxa acts as an intermediary between the vpxd and the hostd.
3. The host invokes required libraries/deamons such as DISKLIB/OSFSd to create vSAN objects (vmdk, snapshot,namespace,vswap…)
4. CLOM (Cluster Level Object Manager Daemon) takes care of the vSAN objects – it decides on the components and witnesses that need to be created and checks if there are enough available resources ( disk groups, free space etc.) to satisfy the policy.
This daemon also talks to the CLOM on other hosts to see what space is available.
After the objects are created CLOM is further responsible for monitoring the objects compliance status.
Templates for Figma
- How to build a website with WordPress and what are the best plugins to use Building a website with WordPress is an excellent choice due to its versatility, ease of use, and a vast array of plugins that enhance functionality. Here’s a comprehensive guide to building a WordPress website, along with recommendations for the best plugins
- Top WordPress Plugins for Managing Ads and Monetizing Your Website Effectively: Why is Ads Management Important for Website Monetization? Strategic ad placement throughout the website enables publishers to maximize ad revenue while ensuring a positive user experience. The positioning of ads is critical in capturing users’ attention without being intrusive or disruptive. By understanding user behavior and preferences, publishers can make informed decisions regarding ad placement to ensure that the ads are relevant and engaging.
- Top Directory Plugins for WordPress to Create Professional Listings and Directories: If you are interested in establishing professional listings and directories on your WordPress website, the following information will be of value to you. This article will present the top directory plugins available for WordPress, which include GeoDirectory, Business Directory Plugin, Sabai Directory, Connections Business Directory, and Advanced Classifieds & Directory Pro.
- The Most Important Stages and Plugins for WordPress Website Development: Developing a WordPress website requires careful planning, execution, and optimisation to ensure it is functional, user-friendly, and effective. The process can be broken into key stages, and each stage benefits from specific plugins to enhance functionality and performance. Here’s a detailed guide to the most important stages of WordPress website development and the essential plugins for each stage.
- .org vs .com: A Top Guide to the Differences in Domain Extension
When you set up a website for a business or a non-profit organisation, you might think the most important part of the address is the actual name. But the domain extension (the bit that comes after the dot) is just as important for telling people what your site is all about. - The Best WordPress Plugins for Image Optimization to Improve Load Times and SEO. The pivotal element lies in image optimization. This discourse delves into the significance of image optimization for websites and its impact on load times. Furthermore, we will delve into the advantages of leveraging WordPress plugins for image optimization, such as streamlined optimization processes, enhanced SEO, expedited load times, and an enriched user experience.
- What is a data center or Internet data center? The term “data center” has become very common due to the role it plays in many of our daily activities. Most of the data we receive and send through our mobile phones, tablets and computers ends up stored in these data centers — which many people refer to as “the Cloud”, in a more generic way.
5. CLOM does all that thinks by communicating to the other nodes through the CMMDS (Cluster Monitoring, Membership and Directory Services).
CMMDS is a directory and content of it is used by other vSAN component technologies (DOM, LSOM) to determine the nodes storing the components of an object and the paths by which those nodes are reachable.
CMMDS also discovers and maintains the vSAN cluster, stores information such as node setup, policies, detecting failures in nodes and network paths.
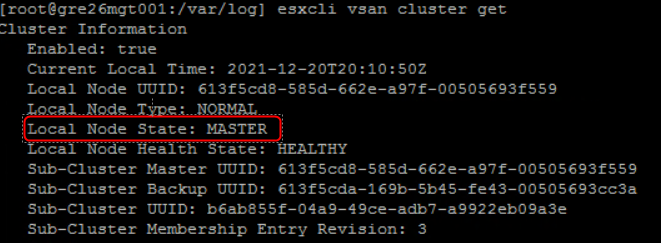
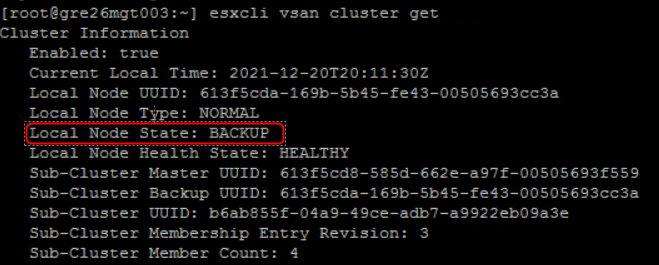
Every host runs CMMDS and one of the vSAN cluster nodes is elected to be a Master. Another one is a Backup node – that holds a copy of the master data – will take over if the Master fails. All other nodes are Agents.
These roles are always system defined and cannot be changed by user/admin.
And here RDT (Reliable Datagram Transport) comes into play as well – the protocol used by vSAN for communication between nodes (cmmds sync, I/O flow). RDT is able to set up and tear down transport connections very quickly, depending on link healthstatus changes that are published by the CMMDS, in order to minimize any delay to the datagram transport as a result of link failures.
Below screenshots from vSAN 4-node cluster (1x master, 1x backup and 2x agents):
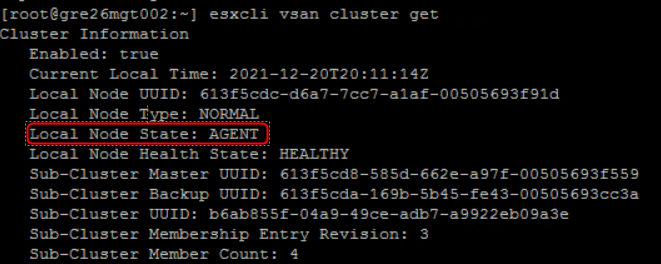
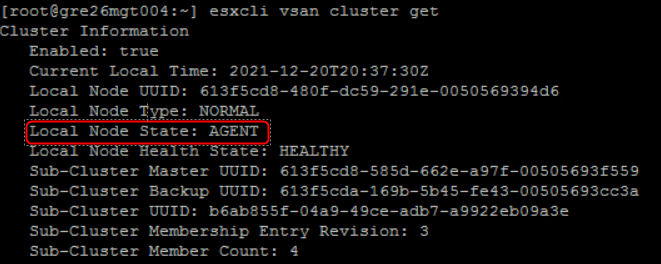
6. If everything looks good then CLOM instructs DOM (Distributed Object Manager) to talk with LSOM (step 7) to create and distribute the objects across the cluster .
DOM is responsible for initial I/O requests and is split up into three processes- Client, Owner, Component Manager.
– DOM Client runs on every node that contains components (runs on the same host as the VM) and performs the I/O to an object – all IO flows from the vSAN client to the owner.
– DOM Owner manages access to the object – determines which processes are allowed to send I/O to the object. Each object in a vSAN cluster has a DOM Owner and DOM Client. Once an object is created one of the vSAN cluster nodes is nominated as the DOM Owner for that object and this host is responsible to handle all IOPS to that object by locating the child components across cluster and redirecting the IO to respective components over vSAN network. The DOM owner may be a host that does not own any component of that object.
DOM Owner distributes data over different hosts through DOM Component Manager which is the local component of the DOM that connects with LSOM on each host.
– DOM Component Manager is responsible for managing the objects on hosts where components exists.
7 – 8. The LSOM ( Local Log-Structured Object Manager) is responsible only for handling the I/O (talking to PSA– Pluggable Storage Architecture which processes the system traffic). It receives I/O from the DOM and ACK when write operations have been completed. The LSOM is responsible as well for cache reading and writing (returns payloads for read operations and handles write buffering) and de-staging of data to capacity tier disks.
And that’s it. Any comments, questions – just ping me 😉